What is UNIVERSE ?
The physical universe is defined as all of space and time (collectively referred to as spacetime) and their contents. Such contents comprise all of energy in its various forms, including electromagnetic radiation and matter, and therefore planets, moons, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. The universe (Cosmos) also includes the physical laws that influence energy and matter, such as conservation laws, classical mechanics, and relativity.
The universe is often defined as "the totality of existence", or everything that exists, everything that has existed, and everything that will exist. In fact, some philosophers and scientists support the inclusion of ideas and abstract concepts—such as mathematics and logic—in the definition of the universe. The word universe may also refer to concepts such as the cosmos, the world, and nature.
Objects in UNIVERSE
Stars
Stars are glowing balls of gas that undergo nuclear fusion; the Sun is a star. Example:
 |
 |
 |
| Alpha Centauri | Antares | Canopus |
 |
 |
 |
| Betelgeuse | Polaris | Sun |
Planets
Planets are moderately large objects orbiting a star. We see planets because they reflect the light of their central star, or in some cases, stars. Planets are generally rocky or gaseous in nature and spherical-shaped. A new group of objects has been recently defined: the Dwarf Planets or Plutoids. These are objects that orbit the Sun, but have not cleared their orbits. Pluto is an example of a Dwarf Planet. Example:
 |
 |
 |
| Mercury | Earth | Mars |
 |
 |
 |
| Jupiter | Uranus | Neptune |
Satellite
A satellite orbits a planet; these objects are also called moons. For example, the Earth’s satellite is the Moon – a proper name. Example:
 |
 |
 |
| Moon | Ganymede | Europa |
 |
 |
 |
| Io | Titan | Callisto |
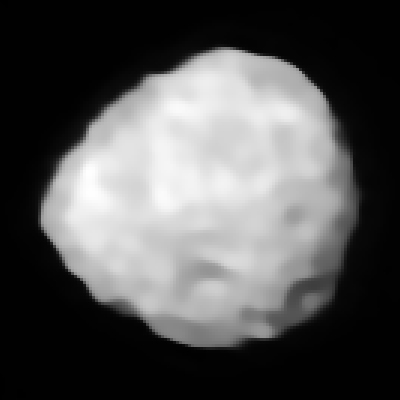
Asteroid
An asteroid is a relatively small, rocky/metallic object usually orbiting a star. Example:
 |
 |
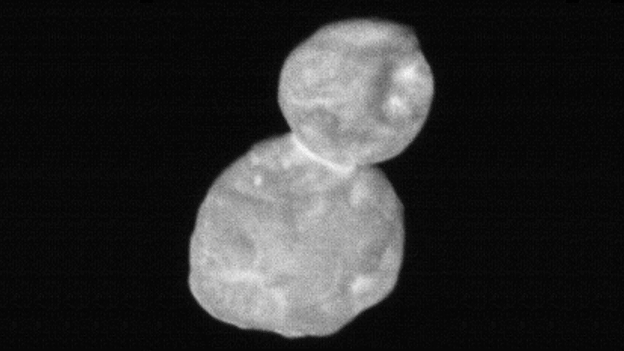 |
| Iris | Bennu | Arrokoth |
 |
 |
 |
| Ryugu | Eros | Interamnia |
Comet
A comet is a relatively small, icy object usually orbiting a star. Asteroids, comets, and miscellaneous small/irregular objects and “dust” are often categorized as Minor Bodies. Example:
 |
 |
 |
| Halley | Borisov | Comet ISON |
Solar System
The Solar System is the Sun and all the objects that orbit the Sun, including the planets and their moons. Our Sun Solar System is only known. Researchers have found others too but they are not recognised as ours. Example:
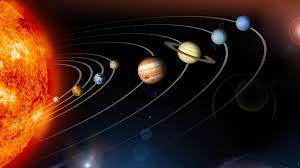 |
| Sun Solar System |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a large island of stars, a few hundred million to over a trillion stars. Example:
 |
 |
 |
| Milky way | Whirlpool | Tadpole |
 |
 |
 |
| Centaurus A | Andromeda | Black eye |
Galactic Cluster
A Galactic Cluster is a collection of galaxies gravitationally bound. Example:
 |
 |
| Virgo | Norma |
Supercluster
A Supercluster is a region where galaxies and galactic clusters are tightly packed. Example:
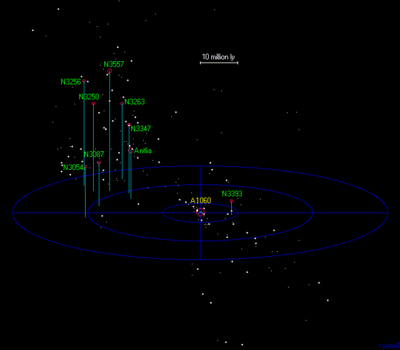 |
| Hydra Centaurus |
Universe
The Universe is all matter and energy, and is also called the Cosmos. Example:
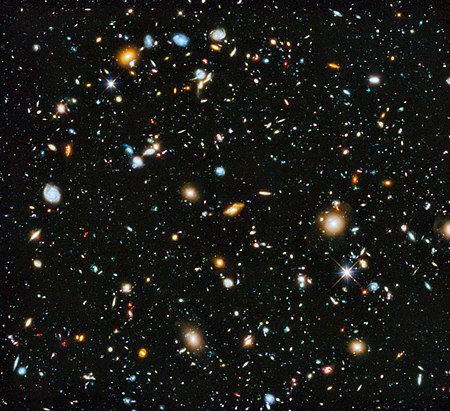 |
| Universe |